What is the Difference Between Block vs Inline Elements
This lesson is a preview from our interactive course
Every HTML element has a different display value, depending on the type of the element. When developing web pages, it's essential to understand the difference between these display values: block and inline.
Block and inline elements serve different purposes and have specific behaviors that can significantly impact the layout and structure of a page. In this lesson, we'll explore the differences between block and inline elements, how to use them effectively, and provide code examples to illustrate their use.
Block Elements#
Block elements are HTML tags that, by default, create a new block-level box on the web page. Each block-level element appears on a new line, and its width automatically expands to fill the available space within its parent container. Some common block-level elements include:
p: Element for creating paragraphs for text content.h1toh6: Elements to act as headings inside the document with varying levels of importance.div: A versatile element that acts as a container to group other elements together.
<h1>Heading</h1>
<p>Initial paragraph</p>
<div>
<p>Paragraph inside a div.</p>
</div>In the above example, all elements are block-level elements. Execute the above code to verify their appearance. You'll notice that all of them appear on a new line.
Note that block-level elements can be nested inside each other.
Inline Elements#
Inline elements, on the other hand, do not create new block-level boxes; instead, they flow alongside adjacent content within the same line. They only take up as much width as necessary to accommodate their content. Some common inline elements include:
a: Element for creating hyperlinks to other documents and resources.strong: Element for adding importance to a text, displayed in bold.em: Element for adding emphasis to a text, displayed in italic.span: A versatile element, similar to thedivtag, but used for inline styling and grouping of text or other inline elements.
<p>
<strong>Inline elements</strong> only take up as much width as necessary.<br />
They also <em>don't break on new lines</em>. Instead, we need to use
<span>br</span> tags. <a href="#top">Go back to top</a>
</p>Unlike block-level elements, inline elements don't start on a new line, nor do they take up the full width of their container.
In the above example, we defined four different inline elements inside a paragraph. As you can see, span elements are displayed without any formatting, just like div elements.

Mixing Block and Inline Elements#
It's common to use both block and inline elements together to create well-structured and visually appealing web pages. Block elements are often used for larger sections of content, such as paragraphs or headings, while inline elements are used within those blocks for more specific formatting or interactive elements. For example:
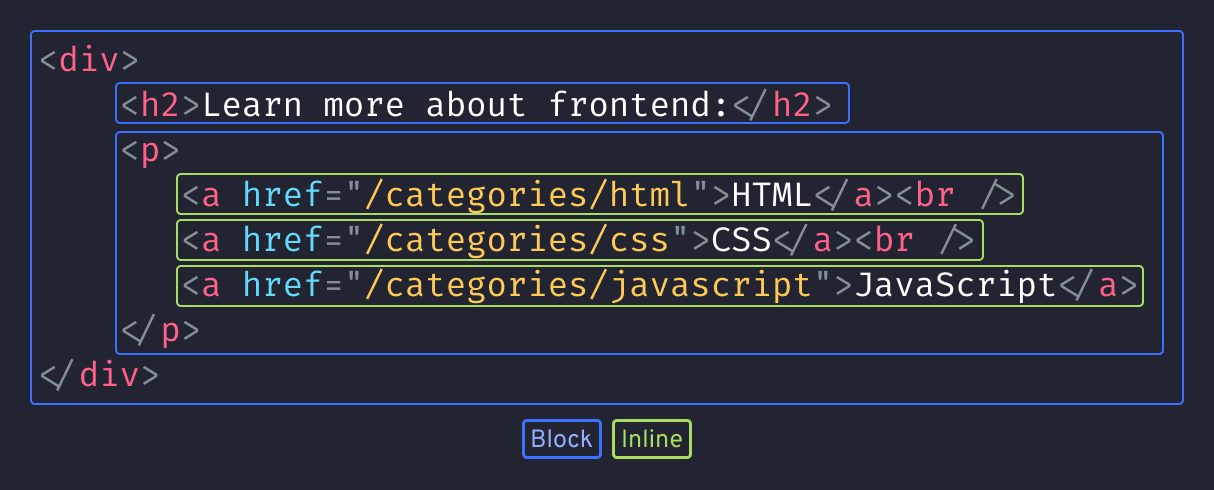
<div>
<h2>Learn more about frontend:</h2>
<p>
<a href="/categories/html">HTML</a><br />
<a href="/categories/css">CSS</a><br />
<a href="/categories/javascript">JavaScript</a>
</p>
</div>In this example, the entire content is wrapped within a div block, which serves as the container. Inside the div, we have a heading for the title, followed by a paragraph containing a list of links. Each line is wrapped in a hyperlink for pointing to a resource.
Make sure you don't use block-level elements inside inline elements.
Summary#
In conclusion, block and inline elements are fundamental building blocks in HTML, each with its unique behavior and purpose. To summarize:
- Block elements: create new block-level boxes and are typically used for larger sections of content and layout structuring. Each new block appears on a new line and fills the available width of its parent container.
- Inline elements: flow within the same line and are ideal for applying specific styles or adding interactive elements to content. They only take up as much width as necessary.
Understanding the distinction between block and inline elements is crucial for creating well-organized and visually appealing web pages. By using these elements effectively and combining them as needed, we can build websites that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing.

Rocket Launch Your Career
Speed up your learning progress with our mentorship program. Join as a mentee to unlock the full potential of Webtips and get a personalized learning experience by experts to master the following frontend technologies: